FUNGAL INFECTION IN CHILDREN : SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, AND CARE TIPS
Fungal Infections in Children
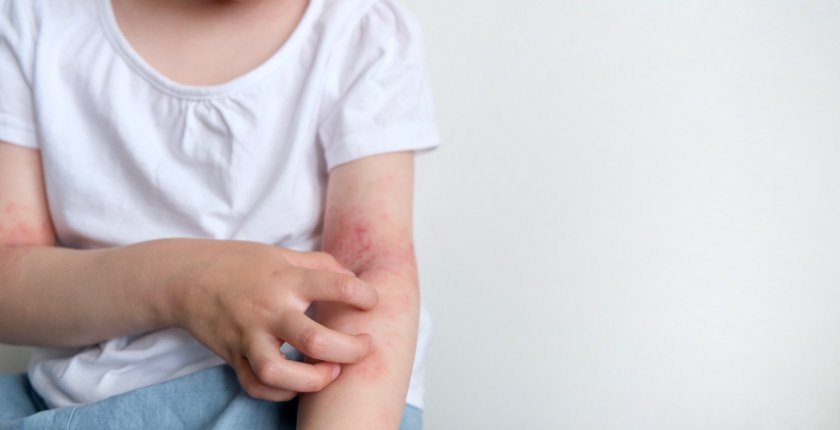
Fungal infections in children are a common issue, yet they often surprise parents. They can manifest as minor infections or escalate to severe infections at any time. Some infections can occur deep in the skin, oral cavity, groin, etc. This article summarises the symptoms, causes, and care tips regarding fungal infections in children. This is a blog on the most common forms of mycoses in children related to symptoms, causative agents, and therapeutic measures. Adequate preventive measures can avert most of the dangers involved with such infections in the case of a child.
Pediatric Mycoses
Primarily, they are known to cause mild infections, but they can cause significant discomfort for children. The following three broad categories of fungi are the primary culprits: The two most common categories of fungi are likely to contain numerous varieties. The first variety uses keratin as its basis for growth. Human skin, nails, and hair are among the various forms this type can take. The second category encompasses yeast and other fungi, such as ringworm, thrush in baby mouths, jock itch, and diaper rash thrush. Each is slightly different in presentation and location.
There are common types of fungal infections in children.
The following list includes some common types of fungal infections in children.
- Ringworm is a highly contagious type of skin infection that typically manifests in a circular form.
- The second suspected infection in a baby’s mouth is oral thrush.
- People describe jock itch as one of the skin infections in the groin, and they claim that it increases with age.
- Many people describe Thrush Diaper Rash as a type of diaper rash that occurs around the diaper region. The cause was Candida yeast.
Symptoms of fungal infections
Understanding the symptomatology of these diseases allows for early disease identification and prompt treatment.
Fungi-caused diseases exhibit unique symptomatology, a trait also shared by some other diseases.
Recognizing Ringworms: Signs and Symptoms
- It appears as a red lesion, round in shape, with a raised scalloped edge.
- The area may be sore and extremely itchy.
- The most common sites are in the body, scalp, and nails.
Identifying Oral Thrush: Symptoms in Infants and Children
- You have white patches on your tongue, cheeks, and gums.
- An infant or child may experience pain or difficulty when bottle-feeding or nursing.
- There is an opening or crease at the corner of the mouth.
Understanding Thrush Diaper Rash: Signs to Look For
- You have a rash over your groin, and your thigh is itching.
- Flaky and peeling skin covers the diaper area.
- The infected diaper area is causing pain and burning sensations
What are thrush and diaper rash symptoms?
Redness in the diaper area marks the condition. Most of the time, this cream appears to be effective in clearing up diaper rash quickly, but it eventually becomes problematic.
These red dots appear both inside and outside of your diaper rash.
Causes of fungal infections in children
Several factors contribute to the onset of fungal infections, ultimately revealing their environmental origins and connections to hygiene practices.
How fungal infections develop: risk factors
Weak Immunity Condition: These children have a condition of weak immunity, which puts them at risk of infection.
This fungus thrives when it grows in favorable, warm, and wet conditions.
He exhibits poor personal hygiene as he struggles to use water for hand washing.
Common Causes of Ringworm Fungal Infection
Direct contact with an affected person or animals can spread this highly virulent ringworm fungus.
Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, towels, dressings, and infected clothes due to illness is a common practice.
Primitiveness of Immunological Defense: Infected individuals have weak immune defense mechanisms in infants or toddlers.
The application of Broadcom antimicrobials disrupts bacteria throughout the body, leading to the dominance of Candida.
Understanding the causes of oral thrush in children is crucial.
- White patches
- Discomfort while feeding
- It mostly appears on the scalp.
Factors Leading to Jock Itch and Diaper Rash
Moistness and Perspiration: The presence of moisture and sweat in the groin and other similar body parts can lead to an attack of jock itch.
Long-Term Use of Nappies: Prolonged use without a diaper change can lead to thrush.
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections
Fungal infections fall into different categories and subgroups. However, the type of fungal infection will determine the most effective treatment for that particular disease. However, the treatment will generally depend on the level and area of the disease.
Effective Ringworm Treatment: Topical and Oral Medications
- Topical antifungal creams: Clotrimazole and Terbinafine
- For most acute types, use either an oral anti-fungal tablet/solution or fluconazole.
Oral Thrush Treatment: Medication Options and Remedies
Medicine: either an oral liquid or topical suspension of Nystatin or suspensions of fluconazole
Oral care: responsive oral care that is going to solve the problem.
Jock Itch Treatment: Managing Symptoms and Prevention
Topical creams containing miconazole or clotrimazole are medications that prevent wetness.
Care Tips for Thrush Diaper Rash: Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Change your nappies often to prevent diaper rash.
Anti-fungal cream:- If the disease is the primary cause, apply the appropriate antifungal creams.
Ringworms in infants
Hygiene practices make it simple for children not to permit the spreading of ringworm fungus in infants’ bodies.
Preventing fungal infections in children
Hygiene Practices to Prevent Ringworm
Do not lend him/his Lend anything to put a comb through the lock upon his head, neither his towels nor clothes. Anti-thrush or thrush. Orally instruct parents. Sterilize your baby’s feeding equipment a bottle feeder, spoon, or pacifier but always sterilize it. Researchers have found that a low-sugar diet restricts the growth of Candida in children.
Preventing Oral Thrush: Tips for Parents
This is a common practice among children. When a mother feeds her baby formula or uses a pacifier, she should immediately wash the nipples and pacifiers in warm water or a dishwasher after each use. This ensures that if there is any yeast on the bottle nipple, the baby won’t contract any infections.
Avoiding Jock Itch: Preventive Measures for Young Boys
Prevention of Thrush Rash among the Young Boys Jock Itch How to prevent dressing care Keep the children in clean, dry clothes, especially after the activity.
Talcum powder: Powder applied on the outer sides of the groin will not allow sweat deposition.
Diaper Care Tips to Prevent Thrush and Diaper Rash
- Diaper Changes Often: Avoid leaving them wet for extended periods.
- Skin Deprivation: Make them diaper-free for some time.
Medical Treatments
Most of them are curable; the remaining ones are very serious, thus needing emergency treatment. If your child is showing signs of recurrent infections or you notice infections spreading, if the pain caused by this infection cannot be relieved in any way, .
When to Seek Medical Advice
- It’s important to recognize when fungal infections require medical attention.
- The patient is not responding within one week to the prescribed treatment.
- The infection keeps on deteriorating and then starts to spread.
- Medical conditions: If the child’s immunization mechanism is not that strong, then he or she should visit a medical doctor.
Paediatrician Consultation: What to Expect
The pediatrician examines the infected body part. He also reviews the patient’s medical history and prescribes specific antibiotics. In some cases, he may even request extreme laboratory tests to determine the specific type of fungus involved.
Self-Care Interventions with Nursing Counselling
A minor infection will heal with the use of home remedies. To initiate any of the aforementioned home treatments, one must first obtain a prescription from a physician.
Home Remedies and Care Tips
Natural Remedies for Fungal Infections in Children
Coconut Oil: Applying the medicine to the affected area stops the children’s bodies from itching.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Home-based Distilled apple cider eliminates the fungus in the children’s bodies.
Care Tips of Parents: Remedies Home Treatment of Symptoms End
Maintenance of Hygiene: Keep the affected area clean and do not pass on the infection. Occasionally, applying a topical cream with antifungal therapy can be beneficial.
Care Tips for Parents: Managing Symptoms at Home
During these times, maintaining proper hygiene and receiving early treatment can effectively control fungal infections in children.
Conclusion
During intensely hot and humid periods, parents may sense a threat to their child’s health, prompting them to assess and implement proper hygiene from the outset, under the guidance of a qualified hygienist. These are not the only options available if the condition persists and exhibits medical signs.