ECZEMA TREATMENTS FOR CHILDREN: SAFE AND EFFECTIVE APPROACHES
Eczema Treatments for Children: Safe and Effective Approaches
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects many children. Managing it can be challenging for parents, but with the right treatments, symptoms can be controlled, and flare-ups reduced. In this guide, we’ll explore safe and effective eczema treatments for children.
Overview of Eczema in Children
Eczema is a chronic condition that causes inflammation, itching, and redness of the skin. While it can appear at any age, it is especially common in young children. Early treatment and care are essential to managing this condition.
What is Eczema?
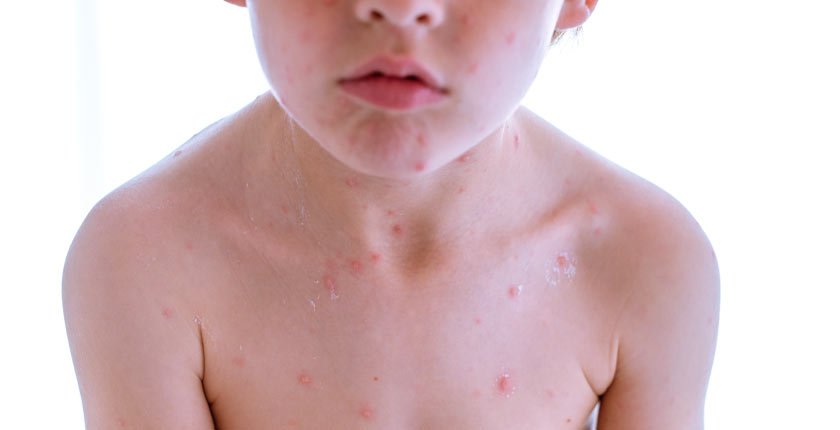
Eczema is a skin condition that results in patches of dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is often linked to allergies or a genetic predisposition and tends to flare up due to certain triggers.
Common Eczema Symptoms in Children
- Dry, itchy skin
- Red or brown patches on the skin
- Raised bumps that may ooze or crust over
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin
Types of Eczema Affecting Children
The most common type of eczema in children is atopic dermatitis, but others include:
- Contact dermatitis:Triggered by contact with irritants.
- Seborrheic dermatitis:Affects oily areas like the scalp.
- Dyshidrotic eczema:Causes small, itchy blisters, primarily on hands and feet.
Causes of Eczema in Children
Eczema can be triggered by various factors such as genetics, environmental irritants, and allergies. Some common triggers include:
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Certain fabrics (like wool or synthetics)
- Changes in weather
- Food allergens
Effective Eczema Treatments for Children
Importance of Moisturizers in Eczema Management
Keeping the skin hydrated is one of the most important steps in managing eczema. Moisturizers help lock in moisture, prevent dryness, and create a protective barrier on the skin.
How Antihistamines Help with Eczema
Antihistamines can help reduce itching, which prevents children from scratching and worsening their eczema. They work by blocking the body’s allergic response.
Safe Use of Antihistamines for Kids
Non-sedating antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) are often recommended for daytime use. Always consult a doctor before administering antihistamines to children to ensure proper dosage.
What is Phototherapy?
Phototherapy involves using controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light to reduce inflammation and itching in children with eczema.
How Phototherapy Benefits Children with Eczema
For children with moderate to severe eczema, phototherapy can significantly reduce symptoms and improve skin appearance. It works by slowing the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation.
Safety Considerations for Children
Phototherapy is generally safe but should be performed under medical supervision. Side effects may include mild sunburn or skin irritation.
Overview of Immunosuppressive Drugs
For severe eczema that does not respond to other treatments, immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed. These drugs work by suppressing the immune system’s overreaction.
When to Use Them in Eczema Treatment
These medications are typically reserved for severe cases of eczema that don’t respond to topical treatments.
Potential Side Effects and Safety
While effective, immunosuppressive drugs can cause side effects like increased susceptibility to infections, so they must be used with caution and under close medical supervision.
Role of Steroid Creams in Eczema Treatment
Topical steroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and control flare-ups in children with eczema. They come in different strengths depending on the severity of the condition.
Guidelines for Safe Use
Steroid creams should only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Avoid using them for long periods, and apply only to affected areas to minimize the risk of side effects such as skin thinning.
Managing Eczema Rash and Symptoms
Strategies to Manage Eczema Rash
To manage eczema effectively:
- Moisturise regularly:Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Use gentle cleansers:Avoid harsh soaps and opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
- Use wet wraps:Soak a cloth in warm water and apply it to the affected area to soothe itching.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Understanding what triggers your child’s eczema is key to preventing flare-ups. Keep a diary of any food, environmental, or stress-related triggers that may worsen symptoms.
Daily Care Routine for Eczema
- Bath daily:Use lukewarm water and mild cleansers.
- Moisturise immediately:After bathing, use a thick cream or ointment.
- Dress in soft fabrics:Avoid itchy or rough materials like wool.
How to Cure Eczema Permanently? Current Treatments and Their Effectiveness
While there is no cure for eczema, treatment can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Moisturizers, topical steroids, and antihistamines are the most effective treatments available.
Emerging Therapies and Research
New therapies, such as biologic drugs, are being researched and show promise in managing severe cases of eczema by targeting specific immune responses that cause the condition.
Eczema on the Face: Special Considerations
Unique Challenges of Facial Eczema
Facial skin is thinner and more sensitive, making it prone to irritation. Special care is needed to manage eczema on theface.
Recommended Treatments for Facial Eczema
Gentle moisturizers and low-strength steroid creams can be used to treat facial eczema. Products containing colloidaloatmeal or natural oils like coconut oil may help soothe irritation.
Conclusion
Eczema in children can be managed effectively with the right treatments and daily care. By using moisturizers, identifying triggers, and following medical advice, parents can significantly reduce their children’s symptoms and improve their quality of life. At Cutis Hospital, we offer specialized eczema care to help your child live more comfortably.
FAQs
1.Can eczema be cured permanently?
Eczema is a chronic condition, but with proper treatment, symptoms can be managed, and flare-ups minimized.
2.What triggers eczema in children?
Common triggers include allergens, stress, dry skin, and certain fabrics or chemicals.
3.Is eczema contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious.
4.Can diet affect eczema?
Certain food allergies, such as dairy or gluten, may trigger eczema in some children.
5.How often should I bathe my child with eczema?
Daily baths with lukewarm water can help manage eczema, but avoid hot water as it can dry out the skin.
6.Can eczema spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, untreated eczema can spread or flare up in new areas of the body.
7.Is eczema linked to asthma?
Yes, children with eczema are more likely to develop asthma or allergies.
8.Are steroid creams safe for children?
Yes, when used as directed by a doctor, low-strength steroid creams are safe and effective for managing eczema.
9.How do I prevent eczema flare-ups?
Regular moisturizing, avoiding known triggers, and maintaining a daily care routine can help prevent flare-ups.
10.Should I see a doctor for my child’s eczema?
If over-the-counter treatments aren’t helping or the eczema is severe, it’s best to consult a dermatologist for specialized care.